Reproductive toxicity
Based on animal studies, siponimod may cause fetal harm. Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception to avoid pregnancy during and for 10 days after stopping siponimod treatment1
For EU and RoW PRIM
| If pregnancy test shows positive, please contact the registry |
For US Registry

As of 25-September-2020, 15 pregnancies were reported from clinical trials2 and none from postmarketing setting3
- Maternal exposure to siponimod during pregnancy was reported in 10 women and 5 women had maternal exposure before pregnancy
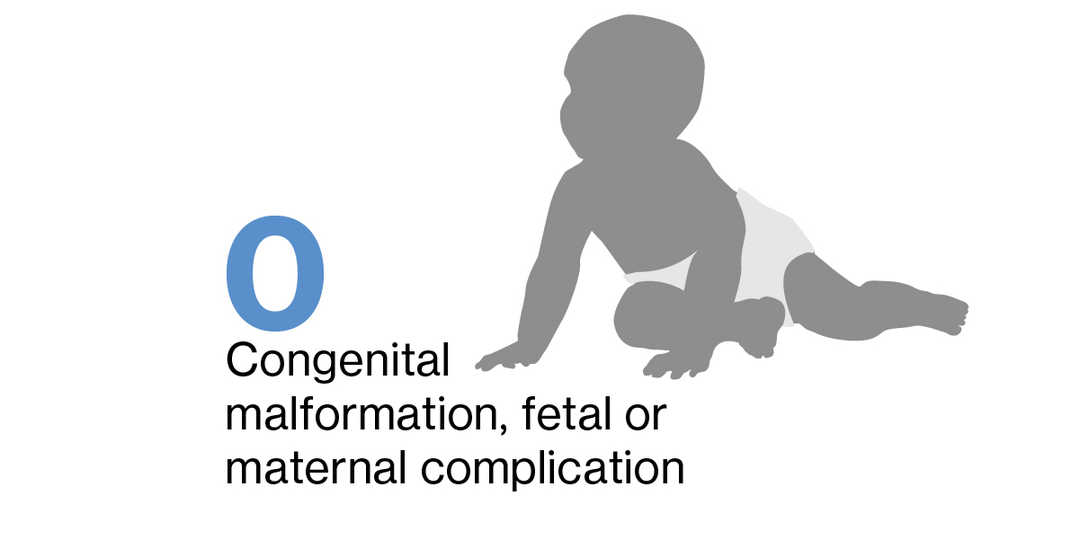
No events of congenital malformation (including major and minor), fetal or maternal complication related to pregnancy and delivery have been reported in pregnant women exposed to siponimod